reduction in area tensile test formula|reduction of area z ductile : inc Reduction of area is the proportional reduction of the cross-sectional area of a tensile test piece at the plane of fracture measured after fracture. R a = A i - A f A i ⋅ 100. where. R a = Precent reduction of area. A i = Cross ectional area . WEB21 de dez. de 2019 · NOTA DE FALECIMENTO É com enorme pesar que a INTERPAX comunica o Falecimento de Fábio Ramos Rodrigues ,aos 35 anos de idade. Seu corpo .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB@housewifeisonyoutube's Biography Public figure. Bay Area well-known lingerie model. Digital creator. I create the hottest lingerie and bikini content.😘 Subscribe to my channel .
Reduction of area is the proportional reduction of the cross-sectional area of a tensile test piece at the plane of fracture measured after fracture. R a = A i - A f A i ⋅ 100. where. R a = Precent reduction of area. A i = Cross ectional area .Tensile testing is described, covering test specimen form, determination of the engineering stress/strain curve, and derivation of test results: ultimate tensile strength, yield point, .In tensile tests on ductile materials, localized necking occurs after the tensile strength is reached. The material ultimately also breaks in this area. The largest change in cross-sectional area in relation to the initial cross-section S o is .
unità di misura dell umidità
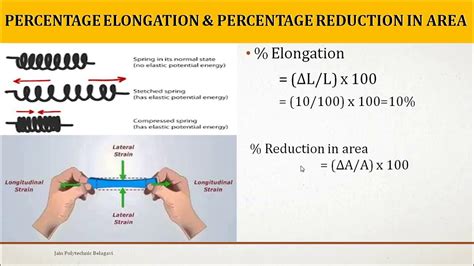
Percent Reduction in Area - The reduction in cross-sectional area of a tensile specimen at fracture = ((initial area - final area)/ initial area) x 100. Percent reduction in area is also a .Purpose. To obtain the material’s stress-strain relationship. To determine the following structural properties: modulus of elasticity, yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, failure strength, and .% Reduction in area - The total percent decrease in the cross-sectional area of a specimen during the tensile test. Tensile strength - The maximum engineering stress experienced by a .Reduction of area, like elongation at break, is a measure of ductility and is expressed in percent. Reduction of area is calculated by measuring the cross sectional area at the fracture point (Az). Reduction of area (%) = (Ao-Az)/Ao .
Percentage reduction of area is another measure of ductility which can be measured in a tensile test. It is obtained by carefully fitting together the ends of the fractured tensile specimen and measuring the dimensions of the .
Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials governs the determination of Ultimate Tensile Strength, Yield Strength plus Elongation and Reduction of Area which are .Use the following formula to calculate elongation: Elongation (%) = 100 x ∆L/Lo . Lo – the original gage length. ∆L – the change in length after subjecting the material to tensile stress and . For instance, if you have a sheet of metal with an initial area of 100 square units and after a process, its area is reduced to 75 square units, the reduction of area can be calculated as follows: \[ ROA = \frac{100 - 75}{100} \times 100 = 25\% \]
Percent Reduction in Area - The reduction in cross-sectional area of a tensile specimen at fracture = ((initial area - final area)/ initial area) x 100. Percent reduction in area is also a measure of ductility. Isotropic – Isotropic materials have elastic properties that are independent of direction. Most common structural materials are . Exploring Elongation TestingElongation testing, a cornerstone of material science, reveals a material's ductility and strength when under tensile stress. By stretching a sample until it breaks, this test measures how much a material can deform before failing. In industries prioritizing safety and durability like automotive and construction, this insight is crucial. . What is a tensile test?In the field of materials science and engineering, a tensile test is a widely used method to determine the mechanical properties of a material, specifically its response to tensile forces. It involves subjecting a specimen to an ever-increasing tensile load until it reaches its breaking point. By measuring the applied force and the resulting deformation . Tensile strengths of 2.0 to 5.0 mol% YâOâ-stabilized ZrOâ polycrystals are described using the newly developed tensile testing method. The tensile test was conducted by attaching three strain .
Tensile Test: The main principle of the tensile test is denotes the resistance of a material to a tensile load applied axially to a specimen. It is very important to the tensile test to be considered is the standard dimensions and profiles are adhered to. The typical progress of tensile test can be seen in figure. tensile test done on utm .
% Reduction in area - The total percent decrease in the cross-sectional area of a specimen during the tensile test. Tensile strength - The maximum engineering stress experienced by a material during a tensile test (ultimate tensile strength). Tensile test - Measures the response of a material to a slowly applied uniaxial force. The Reduction in area is the difference between an original given cross-sectional area of a test specimen before being subjected to tension and the given area of its smallest cross-section after rupture at the conclusion of the test, with the original cross-sectional area expressed as a percentage.Influence of Test Speed; Influence of Tensile Test Equipment; Tensile testing characterizes the forming and structural behavior of sheet metals. The test involves loading a sample with a well-defined shape along the axis in tension, generally to fracture, and recording the resultant load and displacement to calculate several mechanical properties.
Reduction of Area. Measure of the ductility of metals obtained in a tensile test. It is the difference between original cross sectional area of a specimen and the area of its smallest cross section after testing. It is usually ex-pressed as % decrease in original cross section. The smallest cross section can be measured at or after fracture.
Pf ≡ final load carried by the specimen during the test, N (lb) A0 ≡ original cross-sectional area of specimen, mm 2 (in.2) • Calculate the reduction of cross-sectional area. 0 0 %Reduction 100f AA A − =× (1.1.5) where: Af ≡ cross-section after failure, mm 2 (in.2) To calculate the cross-section after failure, fit the ends of the . Ultimate Tensile Stress (UTS) and Ductility. It may be noted at this point that it is common during tensile testing to identify a “strength”, in the form of an “ultimate tensile stress” (UTS).This is usually taken to be the peak on the nominal stress v. nominal strain plot, which corresponds to the onset of necking.
Consider a rod of length L o L_o L o under tensile load along the longitudinal direction. Due to the nature of force, the rod's length would increase, and the area of the cross-section will decrease (learn more with our cross-sectional area calculator). Say the length of the rod under tensile load is L f L_f L f . Tensile or tension testing is a fundamental and most commonly used test for the characterization of the mechanical behavior of materials. The test consists of pulling a sample of material and measuring the load and the corresponding elongation. . The second measurement of ductility is defined as the percentage reduction in area, %RA. It is .Tension test is performed on mild steel, tor steel and high tensile steel to determine the properties like Young's modulus, ultimate strength, and the percentage elongation. . Percentage reduction in the area = (Change in length/Original Area)/100; Procedure for Tension Test on Steel Rod. . The gauge length is calculated by the formula . A tensile test is a type of characterization method performed on an elongated sample with a special geometry defined in a technical standard. In this test, the sample is fixed by both ends to a special machine which can both apply a pulling or tensile force and measure the resulting strain at the same time. The result of this type of test is a .
Stress is a quantity that describes the magnitude of forces that cause deformation. Stress is generally defined as force per unit area. When forces pull on an object and cause its elongation, like the stretching of an elastic band, .Beyond necking, the strain is nonuniform in the gage length and to compute the true stress-strain curve for greater engineering strains would not be meaningful. However, a complete true stress-strain curve could be drawn if the neck area were monitored throughout the tensile test, since for logarithmic strain we haveThe reduction of the cross sectional area. . This is also expressed as a percentage and is calculated using this formula: Reduction of the C.A area (%) = 100 x (Ao – Af)/Ao . Ao is the original cross-sectional area. . While performing the tensile stress test, it’s important to note that temperature is a major factor in the ductility of . The tensile test is used to determine the strength (yield point, ultimate tensile strength) and toughness (elongation at break) of a material! Setup. . reduction in area: measure of the brittle fracture resistance of a material: in general, a high reduction in area value of materials is desirable .
unità di misura della umidita
Fig. 7 is from Fig. 3 and is a modified form of experimental results shown in Fig. 3 [3], [4].It shows that the reduction in area varies with strain rate for Fe17Cr stainless steel tensile tested at temperatures 923 K and 873 K with 5 strain rates respectively, a kind of measurement uncertainty relative to strain rate.For each temperature there is a critical strain rate at which . In the uniaxial tensile test, the true fracture strain or the reduction of area (or thickness) are also regarded as representative indicators of local ductility [1, 8, 3]. Local ductility .The %EL is specific to the tensile testing standard, particularly the ratio of the diameter of a round bar tensile specimen to its parallel length (and to the specified test conditions, rate etc.).Area Reduction (AR) =(A o-A f)/A o Ao F TS = max 4 Elastic Plastic P Deformation Fracture P Gauge necking Length Measuring Displacement; extensometer, strain gauge Measuring Force; Transducer Tensile Test ASTM standards 5 • Engineering Stress & Strain – Original Area, A o • True Stress and Strain – Instantaneous Current Area, A o o e L .
Stress is generally defined as force per unit area. When forces pull on an object and cause . Strain under a tensile stress is called tensile strain, strain under bulk stress is called bulk strain (or volume strain), and that caused by . Compressive stress and strain are defined by the same formulas, Equations \ref{12.34} and \ref{12.35 .Reduction of Area. Measure of the ductility of metals obtained in a tensile test. It is the difference between original cross sectional area of a specimen and the area of its smallest cross section after testing. It is usually ex-pressed as % decrease in original cross section. The smallest cross section can be measured at or after fracture.
what is reduction of area
unità di misura di umidità
tensile testing pdf
tensile testing methods
22 de ago. de 2023 · 3.4K subscribers in the homenagemtrans community. Comunidade criada para os amantes da mais belas mulheres, sejam elas trans ou cis, apreciar sem..
reduction in area tensile test formula|reduction of area z ductile